(a) Scaling specified by the Board.
(1) Scaling between
the U.S. Federal banking capital rules and NAIC RBC.
(i) Scaling
capital requirement. When calculating the building block capital
requirement for a building block parent in accordance with section
217.607, where the indicated capital framework is NAIC RBC or the
U.S. Federal banking capital rules, and where the indicated capital
framework of the appropriate downstream building block parent is NAIC
RBC or the U.S. Federal banking capital rules, the capital requirement
scaling modifier is provided by table 1 to this paragraph (a)(1)(i).
Table 1 to
paragraph (a)(1)(i)—Capital requirement scaling modifiers for
NAIC RBC and the U.S. federal banking capital rules
| |
Upstream building block parent’s indicated capital
framework: |
| NAIC RBC |
U.S. federal banking capital rules |
| Downstream building block parent’s indicated capital framework: |
|
|
| U.S. federal banking capital
rules |
0.0106 |
1 |
| NAIC RBC |
1 |
94.3 |
(ii) Scaling
available capital. When calculating the building block available
capital for a building block parent in accordance with section 217.608,
where the indicated capital framework is NAIC RBC or the U.S. Federal
banking capital rules, and where the indicated capital framework of
the appropriate downstream building block parent is NAIC RBC or the
U.S. Federal banking capital rules, the available capital scaling
modifier is provided by table 2 to this paragraph (a)(1)(ii).
Table 2 to paragraph
(a)(1)(ii)—Available capital scaling modifiers for NAIC RBC
and the U.S. federal banking capital rules
| |
Upstream building block parent’s indicated capital
framework: |
| NAIC RBC |
U.S. federal banking capital rules |
| Downstream building block parent’s indicated capital framework: |
|
|
| U.S. federal banking capital rules |
Recalculated building block capital requirement * 0.063 |
0 |
| NAIC RBC |
0 |
Recalculated building block capital requirement * 5.9 |
| Capital framework: |
|
|
| NAIC RBC |
0 |
Recalculated building block capital requirement * 5.9 |
(2) Scaling to
determine BBA ratio. For purposes of determining the BBA ratio
under section 217.603(b)—
(i) A depository institution
holding company for which the indicated capital framework is the U.S.
Federal banking capital rules scales its building block available
capital and building block capital requirement the common capital
framework by using the methods described in paragraphs (a)(1) of this
section. For purposes of scaling under this paragraph (a)(2)(i), the
downstream building block parent’s indicated capital framework
is the U.S. Federal banking capital rules and the upstream building
block parent’s indicated capital framework is NAIC RBC; and
(ii) A depository institution
holding company for which the indicated capital framework is NAIC
RBC does not scale its building block available capital or building
block capital requirement.
(b) Scaling not specified by the Board
but framework is scalar compatible. Where a scaling modifier
to be used in section 217.607 or section 217.608 is not specified
in paragraph (a) of this section, and the building block parent’s
indicated capital framework (i.e., jurisdictional capital framework)
is scalar compatible, a building block parent determines the scaling
modifier as follows:
(1) Definitions. For purposes of this section, the following definitions apply:
(i) Jurisdictional intervention point. The jurisdictional
intervention point is the capital level, under the laws of the jurisdiction
for its domestic insurers, at which the supervisory authority in the
jurisdiction may intervene as to a company subject its capital framework
by imposing restrictions on distributions and discretionary bonus
payments by the company or, if no such intervention may occur in a
jurisdiction, then the capital level at which the supervisory authority
would first have the authority to take action against a company based
on its capital level.
(ii) Jurisdiction adjustment. The jurisdictional adjustment
is the risk adjustment set forth in table 3 to this paragraph (b)(1)(ii),
based on the country risk classification set by the Organization for
Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) for the jurisdiction.
This adjustment is applied to the jurisdictional intervention point.
Table 3 to paragraph
(b)(1)(ii)—Jurisdictional adjustments by OECD country risk classification
| OECD CRC |
Jurisdictional adjustment (percent) |
| 0-1, including jurisdictions with no OECD country risk classification |
0 |
| 2 |
20 |
| 3 |
50 |
| 4-6 |
100 |
| 7 |
150 |
(2) Scaling capital
requirement. When calculating the building block capital requirement
for a building block parent in accordance with section 217.607, where
the indicated capital framework of the appropriate downstream building
block parent is a scalar-compatible framework for which the Board
has not specified a capital requirement scaling modifier, the capital
requirement scaling modifier is calculated according to the following
formula:
Figure 1. DISPLAY EQUATION
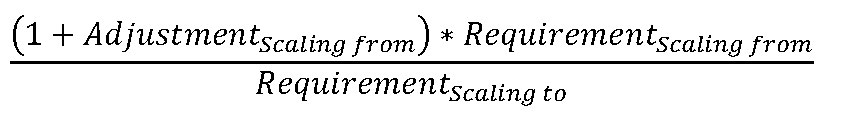
$$
\frac{(1 + \textit{Adjustment}_\textit{Scaling from}) * \textit{Requirement}_\textit{Scaling from}}
{ \textit{Requirement}_\textit{Scaling to} }
$$
Where:
Adjustmentscaling from is equal to the jurisdictional adjustment
of the downstream building block parent;
Requirementscaling from is equal to the jurisdictional intervention point of the downstream
building block parent; and
Requirementscaling to is equal to the jurisdictional intervention point of the upstream
building block parent.
(3) Scaling available
capital. When calculating the building block available capital
for a building block parent in accordance with section 217.608, where
the indicated capital framework of the appropriate downstream building
block parent is a scalar-compatible framework for which the Board
has not specified an available capital scaling modifier, the available
capital scaling modifier is equal to zero.