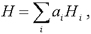(a) General. An originating Board-regulated institution that has
obtained a credit risk mitigant to hedge its securitization exposure
to a synthetic or traditional securitization that satisfies the operational
criteria in section 217.141 may recognize the credit risk mitigant,
but only as provided in this section. An investing Board-regulated
institution that has obtained a credit risk mitigant to hedge a securitization
exposure may recognize the credit risk mitigant, but only as provided
in this section.
(b) Collateral.
(1) Rules of
recognition. A Board-regulated institution may recognize financial
collateral in determining the Board-regulated institution’s risk-weighted
asset amount for a securitization exposure (other than a repo-style
transaction, an eligible margin loan, or an OTC derivative contract
for which the Board-regulated institution has reflected collateral
in its determination of exposure amount under section 217.132) as
follows. The Board-regulated institution’s risk-weighted asset amount
for the collateralized securitization exposure is equal to the risk weighted
asset amount for the securitization exposure as calculated under the
SSFA in section 217.144 or under the SFA in section 217.143 multiplied
by the ratio of adjusted exposure amount (SE*) to original exposure
amount (SE), where:
(i) SE* = max {0, [SE−C × (1−Hs -Hfx)]};
(ii) SE = the amount of the securitization
exposure calculated under section 217.142(e);
(iii) C = the current fair value of
the collateral;
(iv) Hs = the haircut appropriate to the collateral type;
and
(v) Hfx = the haircut appropriate for any currency mismatch between the
collateral and the exposure.
(2)
Mixed collateral. Where the collateral is a basket of different asset types or a basket
of assets denominated in different currencies, the haircut on the
basket will be
Figure 1. DISPLAY EQUATION
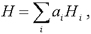
$$
H = \sum_i a_iH_i\text{,}
$$
where
ai is the current fair value of the asset in the basket
divided by the current fair value of all assets in the basket and
Hi is the haircut applicable to that asset.
(3) Standard supervisory haircuts. Unless a Board-regulated institution
qualifies for use of and uses own-estimates haircuts in paragraph
(b)(4) of this section:
(i) A Board-regulated institution must
use the collateral type haircuts (Hs) in Table 1 to section
217.132 of this subpart;
(ii) A Board-regulated institution must
use a currency mismatch haircut (Hfx) of 8 percent if the
exposure and the collateral are denominated in different currencies;
(iii) A Board-regulated
institution must multiply the supervisory haircuts obtained in paragraphs
(b)(3)(i) and (ii) of this section by the square root of 6.5 (which
equals 2.549510); and
(iv) A Board-regulated institution must adjust the supervisory haircuts
upward on the basis of a holding period longer than 65 business days
where and as appropriate to take into account the illiquidity of the
collateral.
(4) Own estimates for haircuts. With
the prior written approval of the Board, a Board-regulated institution
may calculate haircuts using its own internal estimates of market
price volatility and foreign exchange volatility, subject to section
217.132(b)(2)(iii). The minimum holding period (TM) for
securitization exposures is 65 business days.
(c) Guarantees and credit derivatives.
(1) Limitations on recognition. A Board-regulated institution may
only recognize an eligible guarantee or eligible credit derivative
provided by an eligible guarantor in determining the Board-regulated
institution’s risk-weighted asset amount for a securitization exposure.
(2) ECL for securitization exposures. When
a Board-regulated institution recognizes an eligible guarantee or
eligible credit derivative provided by an eligible guarantor in determining
the Board-regulated institution’s risk-weighted asset amount for a
securitization exposure, the Board-regulated institution must also:
(i) Calculate ECL for the protected portion of the exposure using
the same risk parameters that it uses for calculating the risk-weighted
asset amount of the exposure as described in paragraph (c)(3) of this
section; and
(ii)
Add the exposure’s ECL to the Board-regulated institution’s total
ECL.
(3) Rules of recognition. A Board-regulated
institution may recognize an eligible guarantee or eligible credit
derivative provided by an eligible guarantor in determining the Board-regulated
institution’s risk-weighted asset amount for the securitization exposure
as follows:
(i) Full coverage. If the protection amount of the eligible guarantee or eligible credit
derivative equals or exceeds the amount of the securitization exposure,
the Board-regulated institution may set the risk-weighted asset amount
for the securitization exposure equal to the risk-weighted asset amount
for a direct exposure to the eligible guarantor (as determined
in the wholesale risk weight function described in section 217.131),
using the Board-regulated institution’s PD for the guarantor, the
Board-regulated institution’s LGD for the guarantee or credit derivative,
and an EAD equal to the amount of the securitization exposure (as
determined in section 217.142(e)).
(ii) Partial
coverage. If the protection amount of the eligible guarantee
or eligible credit derivative is less than the amount of the securitization
exposure, the Board-regulated institution may set the risk-weighted
asset amount for the securitization exposure equal to the sum of:
(A) Covered portion. The risk-weighted
asset amount for a direct exposure to the eligible guarantor (as determined
in the wholesale risk weight function described in section 217.131),
using the Board-regulated institution’s PD for the guarantor, the
Board-regulated institution’s LGD for the guarantee or credit derivative,
and an EAD equal to the protection amount of the credit risk mitigant;
and
(B) Uncovered portion.
(1) 1.0 minus the ratio of the protection
amount of the eligible guarantee or eligible credit derivative to
the amount of the securitization exposure); multiplied by
(2) The risk-weighted
asset amount for the securitization exposure without the credit risk
mitigant (as determined in sections 217.142 through 146).
(4) Mismatches. The Board-regulated
institution must make applicable adjustments to the protection amount
as required in section 217.134(d), (e), and (f) for any hedged securitization
exposure and any more senior securitization exposure that benefits
from the hedge. In the context of a synthetic securitization, when
an eligible guarantee or eligible credit derivative covers multiple
hedged exposures that have different residual maturities, the Board-regulated
institution must use the longest residual maturity of any of the hedged
exposures as the residual maturity of all the hedged exposures.