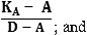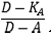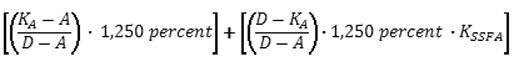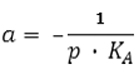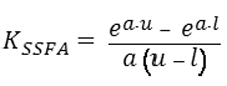(a) General requirements for the SSFA. To use the SSFA to determine
the risk weight for a securitization exposure, a Board-regulated institution
must have data that enables it to assign accurately the parameters
described in paragraph (b) of this section. Data used to assign the
parameters described in paragraph (b) of this section must be the
most currently available data; if the contracts governing the underlying
exposures of the securitization require payments on a monthly or quarterly
basis, the data used to assign the parameters described in paragraph
(b) of this section must be no more than 91 calendar days old. A Board-regulated
institution that does not have the appropriate data to assign the
parameters described in paragraph (b) of this section must assign
a risk weight of 1,250 percent to the exposure.
(b) SSFA parameters. To calculate
the risk weight for a securitization exposure using the SSFA, a Board-regulated
institution must have accurate information on the following five inputs
to the SSFA calculation:
(1) KG is the weighted-average
(with unpaid principal used as the weight for each exposure) total
capital requirement of the underlying exposures calculated using subpart
D of this part. KG is expressed as a decimal value between
zero and one (that is, an average risk weight of 100 percent represents
a value of KG equal to 0.08).
(2) Parameter W is expressed as a decimal
value between zero and one. Parameter W is the ratio of the sum of
the dollar amounts of any underlying exposures of the securitization
that meet any of the criteria as set forth in paragraphs (b)(2)(i)
through (vi) of this section to the balance, measured in dollars,
of underlying exposures:
(i) Ninety days or more past due;
(ii) Subject to a
bankruptcy or insolvency proceeding;
(iii) In the process of foreclosure;
(iv) Held as real
estate owned;
(v)
Has contractually deferred payments for 90 days or more, other than
principal or interest payments deferred on:
(A) Federally-guaranteed
student loans, in accordance with the terms of those guarantee programs;
or
(B) Consumer loans,
including non-federally-guaranteed student loans, provided that such
payments are deferred pursuant to provisions included in the contract
at the time funds are disbursed that provide for period(s) of deferral
that are not initiated based on changes in the creditworthiness of
the borrower; or
(vi) Is in default.
(3) Parameter A is the
attachment point for the exposure, which represents the threshold
at which credit losses will first be allocated to the exposure. Except
as provided in section 142(l) for nth-to-default
credit derivatives, parameter A equals the ratio of the current dollar
amount of underlying exposures that are subordinated to the exposure
of the Board-regulated institution to the current dollar amount of
underlying exposures. Any reserve account funded by the accumulated
cash flows from the underlying exposures that is subordinated to the
Board-regulated institution’s securitization exposure may be included
in the calculation of parameter A to the extent that cash is present
in the account. Parameter A is expressed as a decimal value between
zero and one.
(4) Parameter
D is the detachment point for the exposure, which represents the threshold
at which credit losses of principal allocated to the exposure would
result in a total loss of principal. Except as provided in section
142(l) for nth-to-default credit derivatives, parameter
D equals parameter A plus the ratio of the current dollar amount of
the securitization exposures that are pari passu with the exposure
(that is, have equal seniority with respect to credit risk) to the
current dollar amount of the underlying exposures. Parameter D is
expressed as a decimal value between zero and one.
(5) A supervisory calibration parameter,
p, is equal to 0.5 for securitization exposures that are not resecuritization
exposures and equal to 1.5 for resecuritization exposures.
(c) Mechanics of the SSFA. KG and W are used to calculate KA, the augmented
value of KG, which reflects the observed credit quality
of the underlying exposures. KA is defined in paragraph
(d) of this section. The values of parameters A and D, relative to
KA determine the risk weight assigned to a securitization
exposure as described in paragraph (d) of this section. The risk weight
assigned to a securitization exposure, or portion of a securitization
exposure, as appropriate, is the larger of the risk weight determined
in accordance with this paragraph (c), paragraph (d) of this section,
and a risk weight of 20 percent.
(1) When the detachment point, parameter
D, for a securitization exposure is less than or equal to KA, the exposure must be assigned a risk weight of 1,250 percent;
(2) When the attachment
point, parameter A, for a securitization exposure is greater than
or equal to KA, the Board-regulated institution must calculate
the risk weight in accordance with paragraph (d) of this section;
(3) When A is less than
KA and D is greater than KA, the risk weight
is a weighted-average of 1,250 percent and 1,250 percent times KSSFA calculated in accordance with paragraph (d) of this section.
For the purpose of this weighted-average calculation:
(i) The weight
assigned to 1,250 percent equals
Figure 1. DISPLAY EQUATION
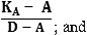
$$\mathrm{\frac{K_A -A}{D - \scriptsize{A}}} \text{; and}$$
(ii)
The weight assigned to 1,250 percent times K
SSFA equals
Figure 2. DISPLAY EQUATION
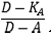
$$
\begin{array}{c c}
\underline{D - K_A} \\
{D - A} & \textrm{.}
\end{array} \\
\text{The risk}
$$
weight will be set equal to:
Risk Weight
= Figure 3. DISPLAY EQUATION
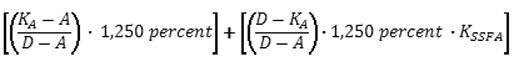
$$
\bigg[ \bigg( \frac{K_A - A}{D-A} \bigg) \cdot \text{1,250 } \mathit{percent} \bigg] +
\bigg[ \bigg( \frac{D-K_A}{D-A} \bigg) \cdot \text{1,250 } \mathit{percent} \cdot K_{SSFA} \bigg]
$$
(d) SSFA equation.
(1) The Board-regulated institution must
define the following parameters:
K A = (1 − W) • K G + (0.5 • W)
Figure 4. DISPLAY EQUATION
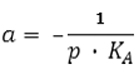
$$
a = - \frac{1}{p \cdot K_A}
$$
u = D − K A
l = max(A − K A, 0)
e = 2.71828, the base of the natural logarithms.
(2) Then the Board-regulated
institution must calculate K
SSFA according to the following
equation:
Figure 5. DISPLAY EQUATION
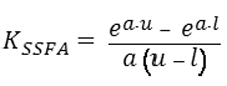
$$
K_{SSFA} = \frac{e^{a \cdot u} - e^{a \cdot l}}{a(u-l)}
$$
(3) The risk
weight for the exposure (expressed as a percent) is equal to K SSFA × 1,250.